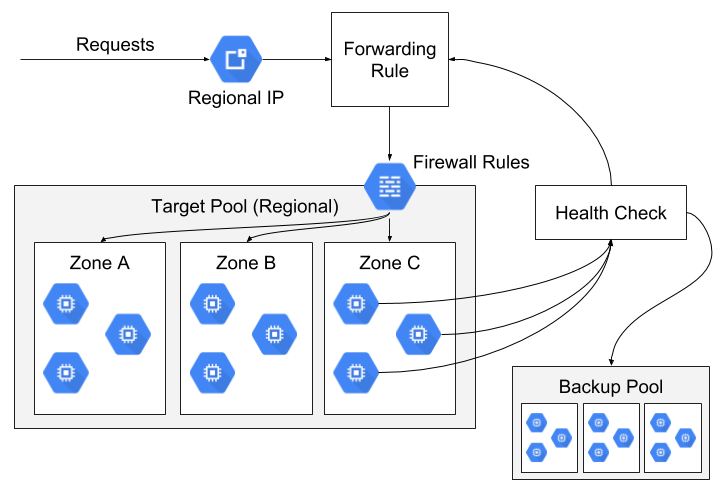
Network load balancers distribute traffic across a set of compute instances known as a target pool. Target pools are regional resources which may contain compute instances across multiple zones within a single region. Each Google Cloud project may have up to 50 target pools. For NLBs, target pools may operate on individual compute instances or on a managed instance group. Because NLB target pools can distribute traffic across arbitrary instances, they’re a good fit for sets of heterogeneous servers.
Target pools can’t be created in the Google Cloud console. You can create a target pool by using the Google Cloud CLI or the API.
Target pools use legacy HTTP health checks.
External passthrough Network Load Balancers can use either a backend service or a target pool to define the group of backend instances. If you’re creating new external passthrough Network Load Balancers, we recommend using backend services.