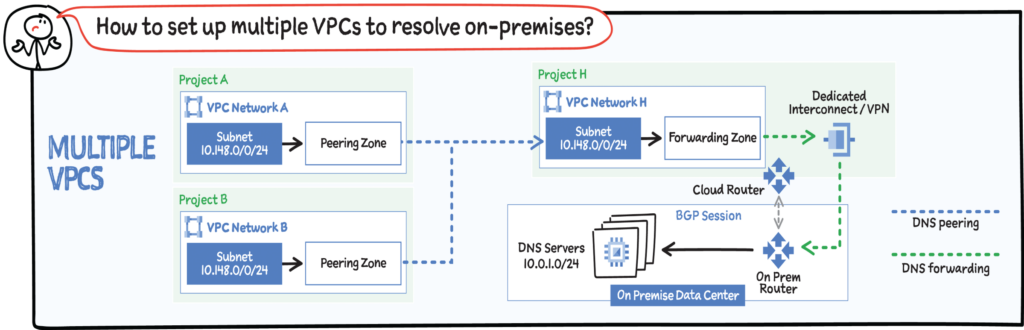
Google Cloud offers inbound and outbound DNS forwarding for private zones. You can configure DNS forwarding by creating a forwarding zone or a Cloud DNS server policy. The two methods are inbound and outbound. You can simultaneously configure inbound and outbound DNS forwarding for a VPC network.
Inbound:
Create an inbound server policy to enable an on-premises DNS client or server to send DNS requests to Cloud DNS. The DNS client or server can then resolve records according to a VPC network’s name resolution order. On-premises clients use Cloud VPN or Cloud Interconnect to connect to the VPC network.
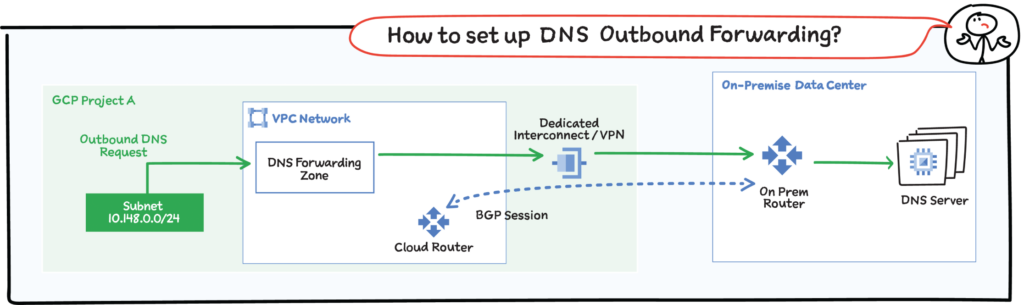
Outbound
You can configure VMs in a VPC network to do the following:
- Send DNS requests to DNS name servers of your choice. The name servers can be located in the same VPC network, in an on-premises network, or on the Internet.
- Resolve records hosted on name servers configured as forwarding targets of a forwarding zone authorized for use by your VPC network.
- Create an outbound server policy for the VPC network to send all DNS requests an alternative name server.